Matlab Continue to Increase Matrix Size

Introduction to Matrix in Matlab
The matrix in Matlab is a type of variable that is used for mathematical computation purposes. Matlab, known as Matrix Laboratory, efficiently processes matrix calculations. Matrix is a two-dimensional array part of linear algebra associated with analytics. Matlab provides inbuilt functionality for creating the matrix and assigning the values to it. There are several mathematical and trigonometric computations supported by Matlab software. Some arithmetic operations on the matrix in Matlab are addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Similarly, it supports tan, cos, sin, cosec, sec, cot, and sin inverse operations. Also, complex numbers computation and concatenation operations for two matrix values.
Matrix Formation
- First, we will see how to create an array in Matlab. An array is a row vector, so to create array commands will be X = [ 1 4 7 6 ]
- In the above example, there are four elements in one row. Therefore, an array name is ' x.'
- An array is a one-dimensional quantity. To create a matrix, we need to specify a two-dimensional array; let us consider one example Matrix A is
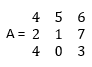
To create the above matrix in MatLab, commands will be
A = [ 4 5 6 ; 2 1 7 ; 4 0 3 ]
- In this elements are written in square brackets ( ' [ ] ' ) and each row separated by semicolon ( ' ; ' ) .
- Screen 1 shows the formation of a matrix that illustrates the above example.
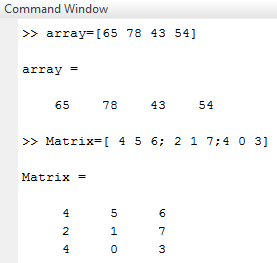
Screen 1: Matrix in Matlab
- Another way to create a matrix is by using commands zeros, ones, etc.
Example : a=zeros(4,1)
A= 0
0
0
0
- Inside the brackets, 4 means four rows, and 1 is a number of a column.
a=ones(2,3) … … … Two rows and three columns.
Ouput:

Screen 2: Matrix in Matlab
Operations on Matrix
Below are the different operations on the matrix:
1. Arithmetic Operation
It allows all arithmetic operations on a matrix, such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, etc.
Syntax: matrix name operator arithmetic constant
Example:
If a is a four by four matrix with values
4 7 3
4 2 7
8 7 2
4 2 1
In Matlab it will be represented as a = [ 4 7 3 ; 4 2 7 ; 8 7 2 ; 4 2 1 ]
a + 10
It will give output as
14 17 13
14 12 17
18 17 12
14 12 11
For
a – 2
Output will be
2 5 1
2 0 5
6 5 0
2 0 -1
The above example is shown on screen 3

Screen 3: Arithmetic operations
2. Trigonometric Operations
In this, we can use all trigonometric operators like sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, cot, sin inverse, etc
Consider one matrix B.
B =5 6 4
3 2 8
Matlab program will be
B = [ 5 6 4 ; 3 2 8 ]
sin ( B )
cos (B )
Output is

Screen 4: Trigonometric Operations
3. Transpose of Matrix
A single quote ( ' ) is used to find the transpose of the matrix.
Let us consider matrix X =
![]()
By applying command X.'
It will give transpose output as
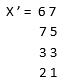
The above example is illustrated on screen 5

Screen 5: Transpose of Matrix
4. Matrix Multiplication
We can perform matrix multiplication. By using the multiplication operator, we can multiply two matrices.
Let us consider X is
6 7 3 2
7 5 3 1
And transpose of X is
6 7
7 5
3 3
2 1
Matrix multiplication is given on screen 6.
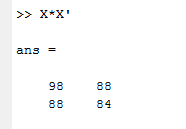
Screen 6: Multiplication of Matrix
5. Power
To find power of any variable dot operator ( ' . ' ) is used before power operator ,Let us consider Matrix X = [ 6 7 3 2 ; 7 5 3 1 ]
X . ^ 3 =
216 343 27 8
343 125 27 1
6. Concatenation
Concatenation is used to join two matrices, and square brackets [ ] are used for the concatenation operator.
Let us consider one example Matrix A is
4 2
5 7
B= [A,A]
The output will be B
4 2 4 2
5 7 5 7
7. Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are a mixture of two parts. Real parts and imaginary parts are generally used to represent imaginary parts ' I ' and ' j ' variables.
If we put square root operation in MatLab command window ( sqrt ( -1 ) ) then it gives output as 0.0000 + 1.0000 i
Here 0 is the real part, and 1 is an imaginary part.
Complex numbers representation is as follows ;
A = [ 5 + 3 i , 5 ; 2 + 2 i , 3 + 1 i ]
It is a two by-two matrix; the output will be
5 + 3 i 5
2 + 2 i 3 + i
The above example is illustrated on screen 7
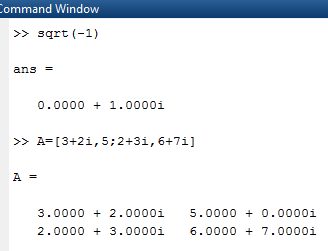
Screen 7: Complex Numbers
8. Size
This command is used to find the size of the matrix. It gives the size in the form of rows and columns. (number of rows and number of columns).
Let us consider example A = [ 5 6 8 2 ; 6 5 4 3 ; 8 7 2 2 ]
Output for size (A) will be 3 4
Here 3 represents no of rows, and 4 represents no of columns.

Screen 8: Size of Matrix
Conclusion
- In matrix arithmetic, addition and subtraction are easy, but multiplication is a challenging task. MatLab makes it simple, and MatLab is specially designed for matrix manipulations.
- All the operations can be easily performed in MatLab, such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, trigonometric functions, cross multiplication, matrix transpose, matrix inverse, complex numbers, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matrix in Matlab. Here we discuss different mathematical operations in the matrix in detail. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Transfer Functions in Matlab
- Data Types in MATLAB
- Matlab Operators
- What is Matlab?
- MATLAB Functions
- Matlab Compiler
olsenoutterculd1988.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.educba.com/matrix-in-matlab/
0 Response to "Matlab Continue to Increase Matrix Size"
Post a Comment